Multi-Language Implementation Guide
Before We Start
This document explains how to set up and manage multiple languages within your UI using a single, globally accessible language variable. It covers the logic behind structuring data sources so that each element can seamlessly adapt to any chosen language.
Locale Setup
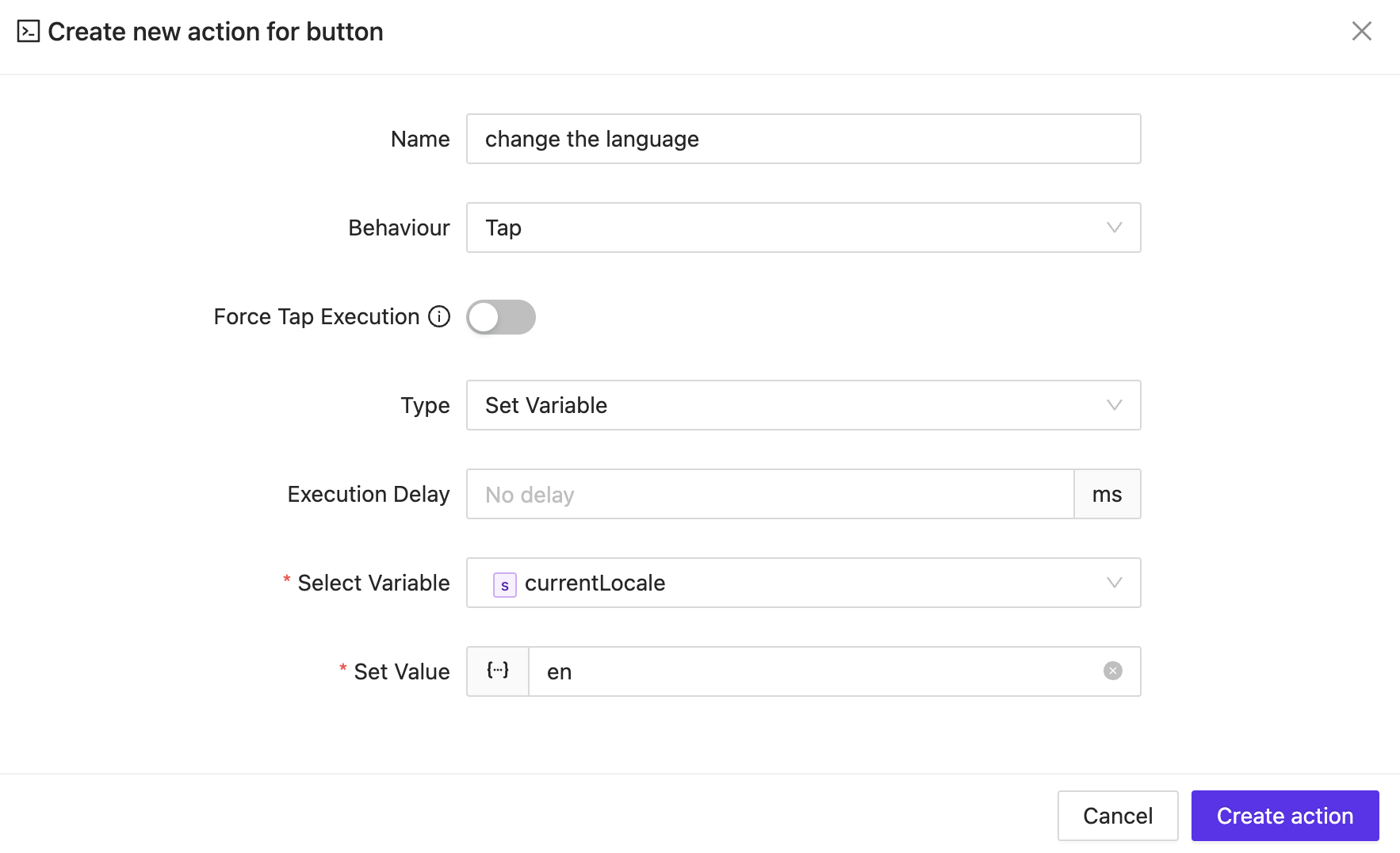
We need a locale variable to store the current language using standard international language codes (e.g., en for English, es for Spanish, or fr for French).
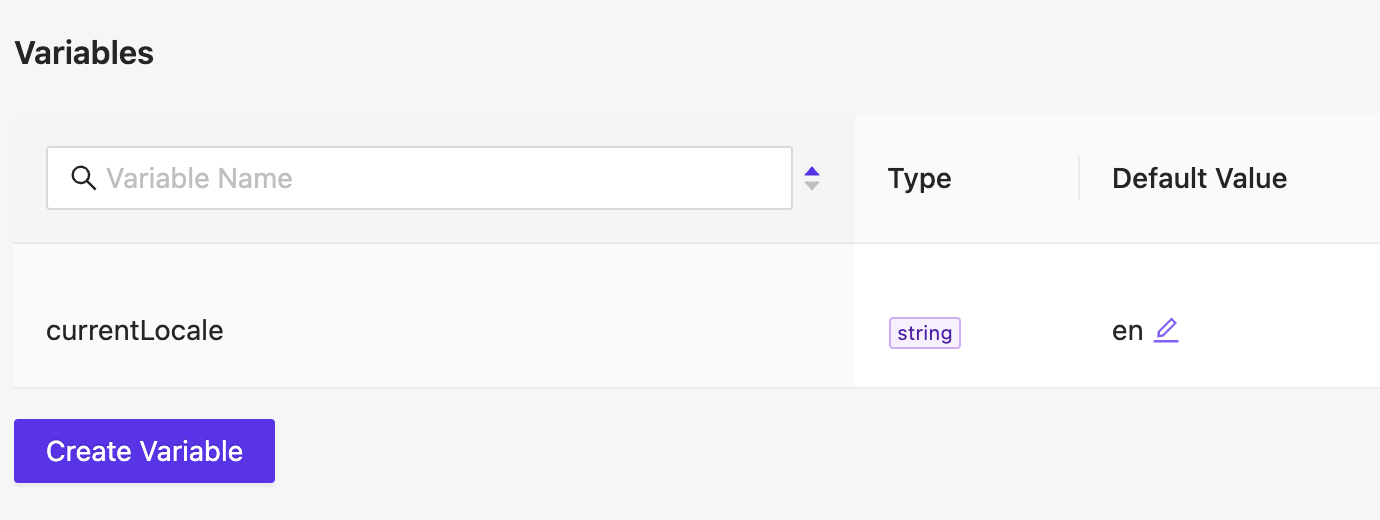
Defining Language-Dependent Components
To support language switching on the fly, define all language-dependent UI components via a datasource. This ensures that changing the language variable globally will update the entire UI.
Structuring Your Datasource
Each datasource used for elements should keep language-specific data together with its matching language code. This approach allows you to handle different languages without manually updating every element.
Below is an example of such a datasource:
{
"rooms": [
{
"id": 1,
"localization": [
{
"language": "en",
"value": "office"
},
{
"language": "es",
"value": "oficina"
}
],
"joinNumber": 23
},
{
"id": 2,
"localization": [
{
"language": "en",
"value": "bedroom"
},
{
"language": "es",
"value": "dormitorio"
}
],
"joinNumber": 24
}
]
}
Single Element Case
Selecting a Single Portion of Data
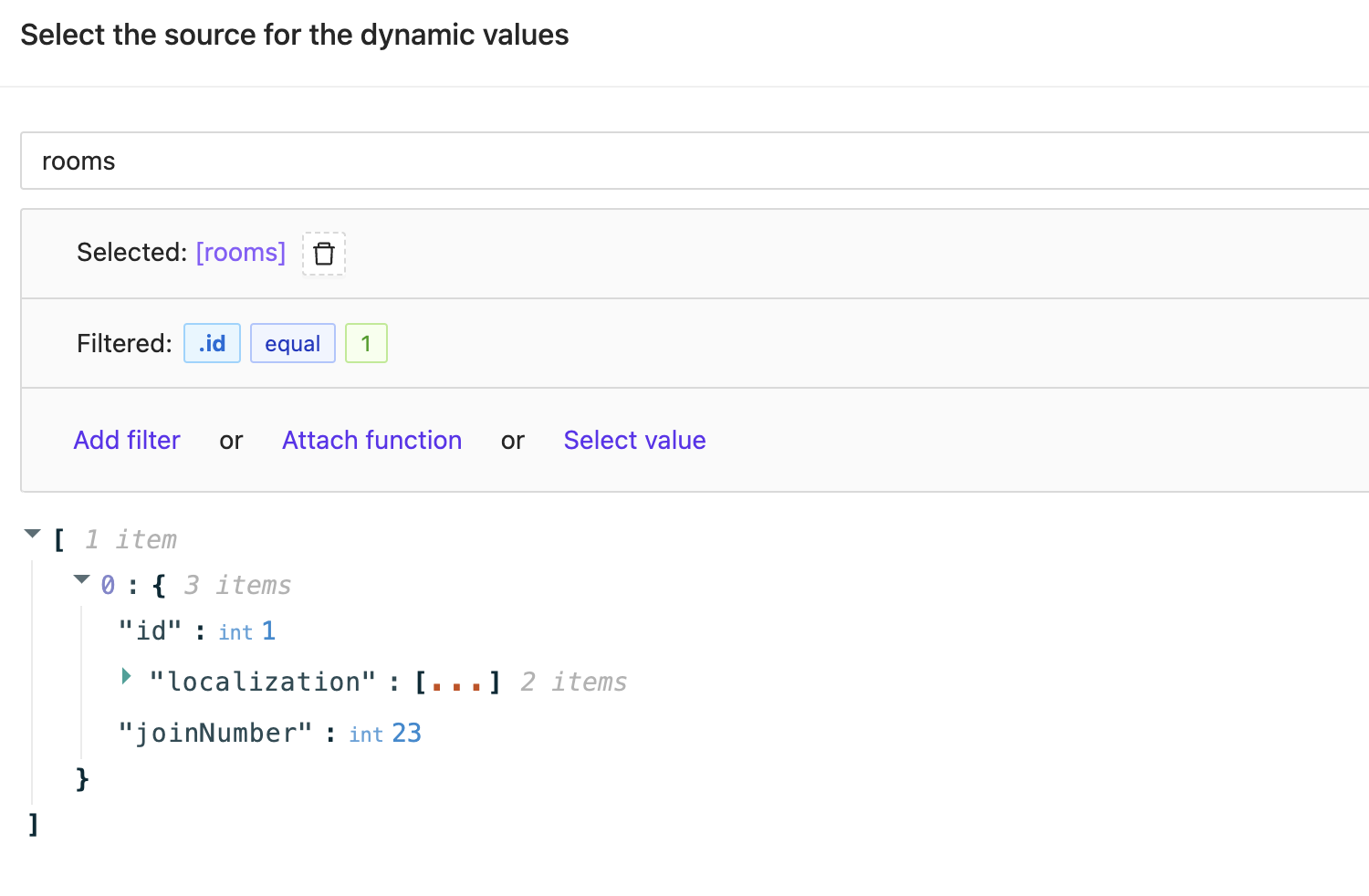
In some scenarios, you only need a single item from the datasource to attach it to the single UI element. For instance, if you filter or directly select a single room object, it might look like this:
{
"id": 1,
"localization": [
{
"language": "en",
"value": "office"
},
{
"language": "es",
"value": "oficina"
}
],
"joinNumber": 23
}
Creating a Function to Select the Language Value
You can create a function (e.g., languageselector) in the Functions section of AVStudio. This function will:
- Retrieve the current language (using the previously defined
currentLocalevariable). - Find and return the matching language value from the object’s
localizationarray. - Remove the original
localizationfield to avoid redundancy.
function languageselector(json) {
/* The function starts by getting the current language setting
from the avgatorStudio. */
const current_language = window?.avgatorStudio?.getVariableByName({
name: 'currentLocale'
});
/* The function assumes the input 'json' is an array and takes
the first element, storing it in 'value'. */
const value = json[0];
/* It searches through the 'localization' array in 'value' to
find the object matching the current language. Then it
extracts the 'value' field from it. */
const localization = value?.localization?.find(
(item) => item?.language === current_language
)?.value;
/* Delete the 'localization' field from 'value' to avoid
duplicating information. */
delete value["localization"];
/* Finally, return a new object with 'data' (remaining fields)
and 'localization' (the selected language value). */
return {
"data": value,
"localization": localization
};
}
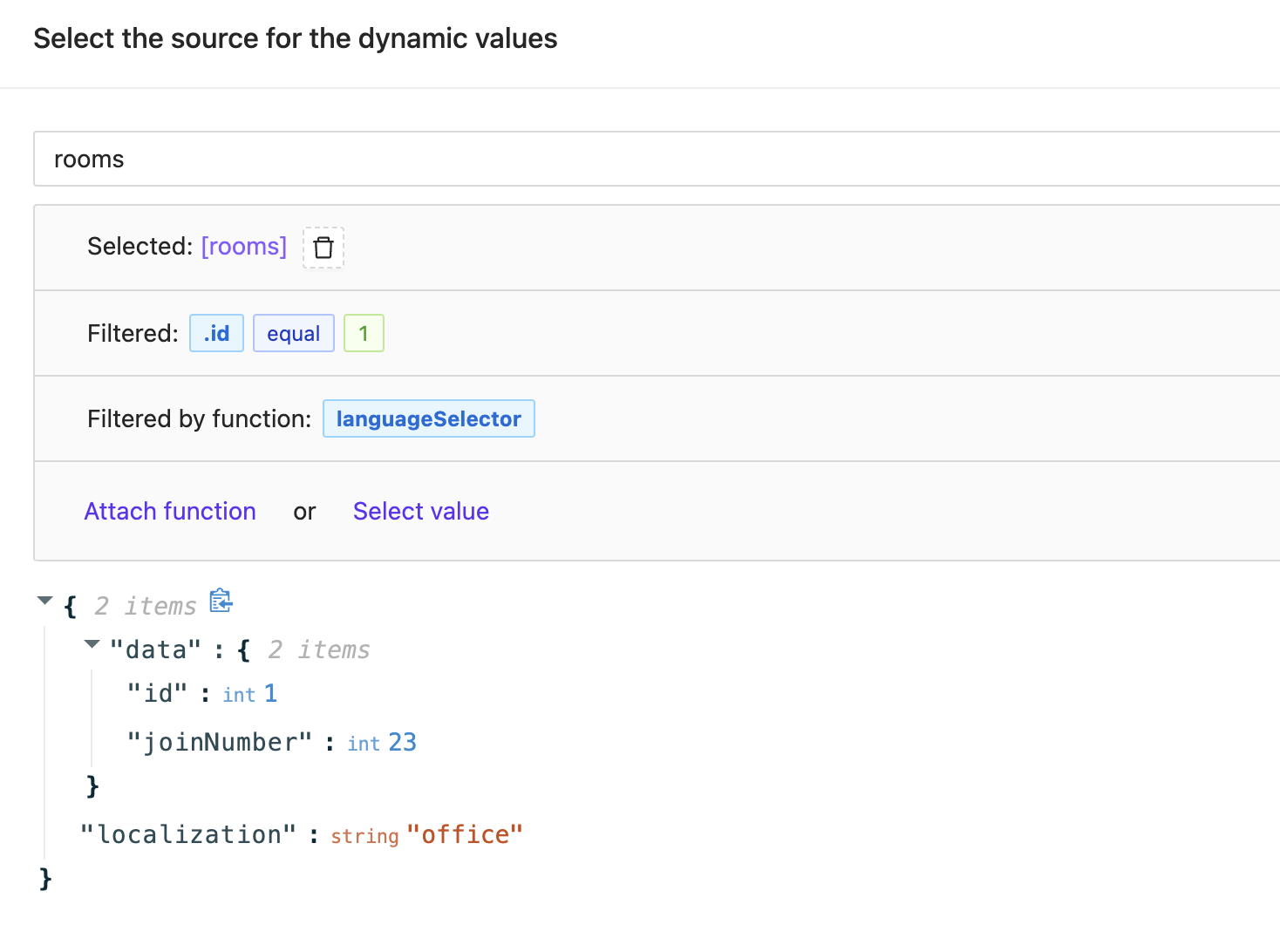
Example Result
Applying this function to the single room object above results in:
{
"data": {
"id": 1,
"joinNumber": 23
},
"localization": "office"
}
Dealing with Subpages List
For a list of subpages (e.g., multiple rooms), modify the function to operate on each item in the array:
function listlanguageselector(json) {
// Retrieve the current language setting from the avgatorStudio object.
const current_language = window?.avgatorStudio?.getVariableByName({
name: 'currentLocale'
});
// Use 'map' to process each item in the JSON array.
return json.map(value => {
// Find the localization matching the current language.
const localization = value?.localization?.find(
(item) => item?.language === current_language
)?.value;
// Remove the 'localization' field from the item to avoid duplication.
delete value["localization"];
// Return the remaining data alongside the selected localization value.
return {
"data": value,
"localization": localization
};
});
}
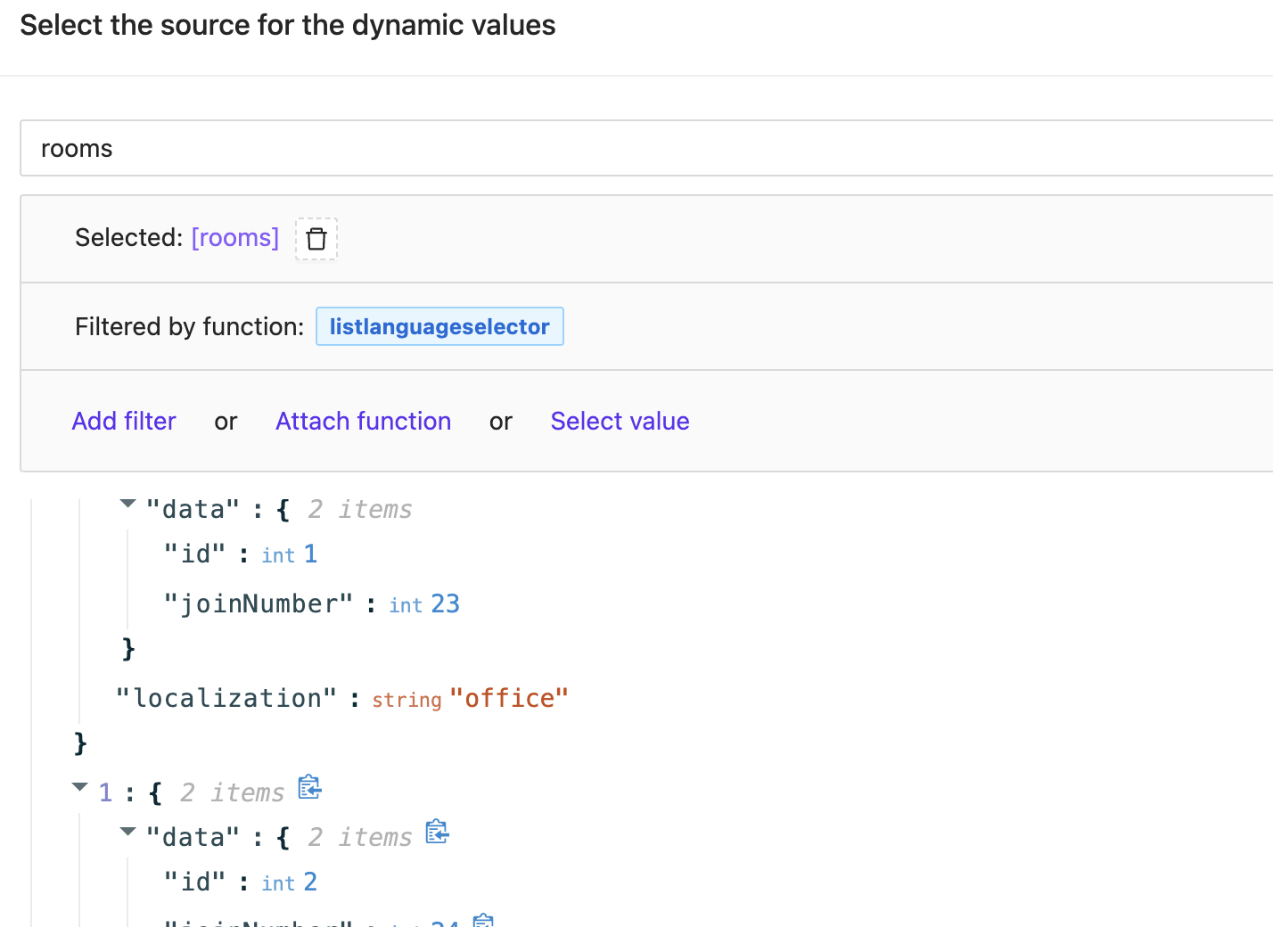
Example Result
When you apply the function to the datasource in subpages list's source selection, you will get a transformed array. For example:
[
{
"data": {
"id": 1,
"joinNumber": 23
},
"localization": "office"
},
{
"data": {
"id": 2,
"joinNumber": 24
},
"localization": "bedroom"
}
]
Updating the Current Locale
If you change the currentLocale variable (in any way supported by AVStudio), all interfaces and components that rely on this logic will automatically reflect the new language settings.