Data Sources in AVstudio
Data Sources serve as JSON-format data repositories that can be either local or populated from external sources via REST API requests.
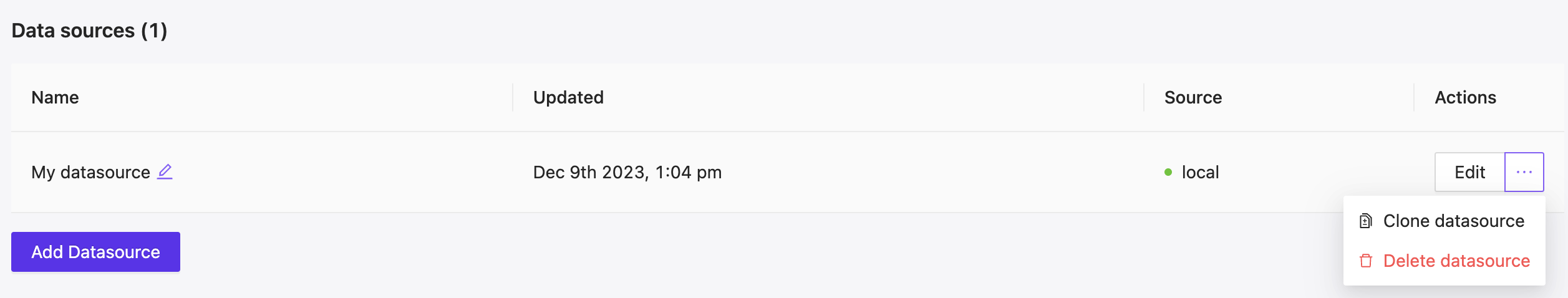
Types of Data Sources
1. Local Data Sources
- Stored within the project
- Data defined during creation
- Static and immutable
- Best for constant data
2. Remote Data Sources
- Data fetched via HTTP/REST API
- Dynamic content updates
- Processor feedback-driven updates
- Configurable request headers
3. Mixed Data Sources
- Combines remote and local storage
- Fallback to local copy if remote fails
- Automatic failover mechanism
- Enhanced reliability
Data Immutability
Data Source content is immutable during runtime. Updates require either a new remote fetch or manual local data modification.
Creating a Data Source
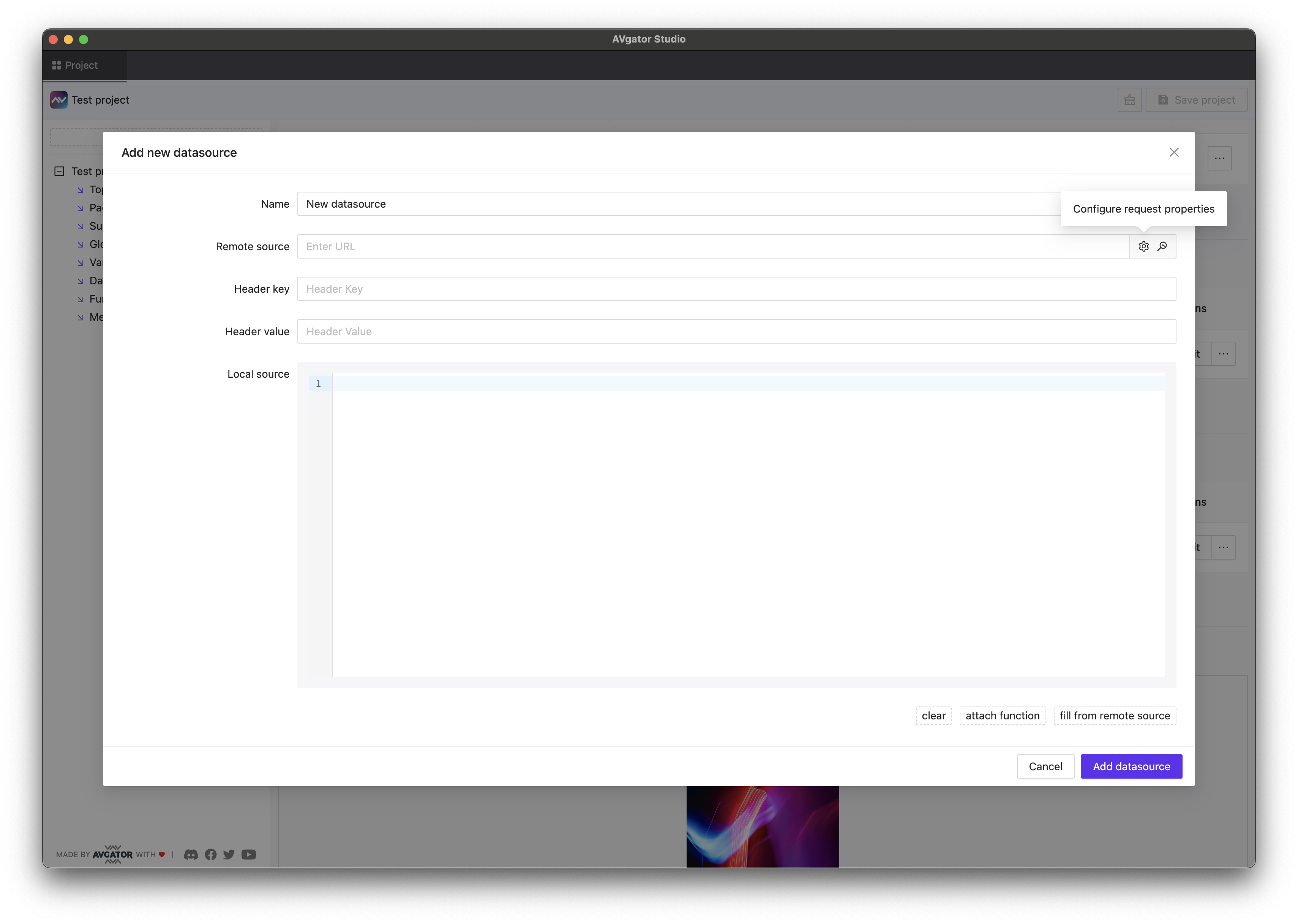
Required Fields
- Name: Unique identifier for the data source
- Type: Local, Remote, or Mixed
Remote Configuration
Optional for Local Data Sources:
- URL: Endpoint for data retrieval
- Header Key: Request header name
- Header Value: Request header value
Local Configuration
Optional for Remote Data Sources:
- JSON Data: Local data storage
- Fallback Data: Backup for remote sources
Global Values
You can use project-level global values for header values and base URLs.
Advanced Features

Data Management
- Clear: Reset local JSON data
- Function Attachment: Transform data structure
- Remote Fill: Populate local storage from remote
Function Integration
- Attach custom functions
- Transform data representation
- Modify data structure
- Apply business logic
Remote Source Management
- Test remote connections
- Monitor data updates
- Configure timeout settings
- Handle error scenarios
Mixed Mode Behavior
When using mixed mode:
- System attempts remote fetch first
- Falls back to local copy if remote fails
- Automatically manages data synchronization
Best Practices
-
Data Structure
- Use consistent JSON formats
- Define clear data schemas
- Document data structures
- Plan for scalability
-
Error Handling
- Implement fallback strategies
- Monitor remote source availability
- Log connection issues
- Test failure scenarios
-
Performance
- Optimize data payload size
- Cache when appropriate
- Monitor response times
- Plan for throttling